At Northeastern University, we create the conditions for robust, deep and flexible learning that will prepare our students for a life of fulfillment and accomplishment in a world that is continually changing. While learning happens in classroom, lab and studio situations, it is much more powerful and robust when students have opportunities to use their knowledge and practice their skills in authentic, real-world situations. Below are listed the expected learning outcomes for our nursing students by program.
Download the Program Learning Outcomes [PDF]
Pre-licensure Nursing Program Data [PDF]
Accelerated Bachelor of Science in Nursing and Bachelor of Science in Nursing
Knowledge for Nursing Practice
- 1.1a Identify concepts, derived from theories from nursing and other disciplines, which distinguish the practice of nursing.
- 1.1b Apply knowledge of nursing science that develops a foundation for nursing practice.
- 1.1c Understand the historical foundation of nursing as the relationship developed between the individual and nurse.
- 1.1d Articulate nursing’s distinct perspective to practice.
- 1.2a Apply or employ knowledge from nursing science as well as the natural, physical, and social sciences to build an understanding of the human experience and nursing practice.
- 1.2b Demonstrate intellectual curiosity.
- 1.2c Demonstrate social responsibility as a global citizen who fosters the attainment of health equity for all.
- 1.2d Examine influence of personal values in decision making for nursing practice.
- 1.2e Demonstrate ethical decision making.
- 1.3a Demonstrate clinical reasoning.
- 1.3b Integrate nursing knowledge (theories, multiple ways of knowing, evidence) and knowledge from other disciplines and inquiry to inform clinical judgment.
- 1.3c Incorporate knowledge from nursing and other disciplines to support clinical judgment.
Person-Centered Care
- 2.1a Demonstrate qualities of empathy.
- 2.1b Demonstrate compassionate care.
- 2.1c Establish mutual respect with the individual and family.
- 2.2a Demonstrate relationship-centered care.
- 2.2b Consider individual beliefs, values, and personalized information in communications.
- 2.2c Use a variety of communication modes appropriate for the context.
- 2.2d Demonstrate the ability to conduct sensitive or difficult conversations.
- 2.2e Use evidence-based patient teaching materials, considering health literacy, vision, hearing, and cultural sensitivity.
- 2.2f Demonstrate emotional intelligence in communications.
- 2.3a Create an environment during assessment that promotes a dynamic interactive experience.
- 2.3b Obtain a complete and accurate history in a systematic manner.
- 2.3c Perform a clinically relevant, holistic health assessment.
- 2.3d Perform point of care screening/diagnostic testing (e.g. blood glucose, PO2, EKG).
- 2.3e Distinguish between normal and abnormal health findings.
- 2.3f Apply nursing knowledge to gain a holistic perspective of the person, family, community, and population.
- 2.3g Communicate findings of a comprehensive assessment.
- 2.4a Synthesize assessment data in the context of the individual’s current preferences, situation, and experience.
- 2.4b Create a list of problems/health concerns.
- 2.4c Prioritize problems/health concerns.
- 2.4d Understand and apply the results of social screening, psychological testing, laboratory data, imaging studies, and other diagnostic tests in actions and plans of care.
- 2.4e Contribute as a team member to the formation and improvement of diagnoses.
- 2.5a Engage the individual and the team in plan development.
- 2.5b Organize care based on mutual health goals.
- 2.5c Prioritize care based on best evidence.
- 2.5d Incorporate evidence-based intervention to improve outcomes and safety.
Population Health
- 3.1a Define a target population including its functional and problem-solving capabilities (anywhere in the continuum of care).
- 3.1b Assess population health data.
- 3.1c Assess the priorities of the community and/or the affected clinical population.
- 3.1d Compare and contrast local, regional, national, and global benchmarks to identify health patterns across populations.
- 3.1e Apply an understanding of the public health system and its interfaces with clinical health care in addressing population health needs.
- 3.1f Develop an action plan to meet an identified need(s), including evaluation methods.
- 3.1g Participate in the implementation of sociocultural and linguistically responsive interventions.
- 3.1h Describe general principles and practices for the clinical management of populations across the age continuum.
- 3.1i Identify ethical principles to protect the health and safety of diverse populations.
- 3.2a Engage with other health professionals to address population health issues.
- 3.2b Demonstrate effective collaboration and mutual accountability with relevant stakeholders.
- 3.2c Use culturally and linguistically responsive communication strategies.
- 3.3a Describe access and equity implications of proposed intervention(s).
- 3.3b Prioritize patient-focused and/or community action plans that are safe, effective, and efficient in the context of available resources.
- 3.4a Describe policy development processes.
- 3.4b Describe the impact of policies on population outcomes, including social justice and health equity.
- 3.4c Identify best evidence to support policy development.
- 3.4d Propose modifications to or development of policy based on population findings.
- 3.4e Develop an awareness of the interconnectedness of population health across borders.
- 3.5a Articulate a need for change.
- 3.5b Describe the intent of the proposed change.
- 3.5c Define stakeholders, including members of the community and/or clinical populations, and their level of influence.
- 3.5d Implement messaging strategies appropriate to audience and stakeholders.
- 3.5e Evaluate the effectiveness of advocacy actions.
- 3.6a Identify changes in conditions that might indicate a disaster or public health emergency.
- 3.6b Understand the impact of climate change on environmental and population health.
- 3.6c Describe the health and safety hazards of disasters and public health emergencies.
- 3.6d Describe the overarching principles and methods regarding personal safety measures, including personal protective equipment (PPE).
- 3.6e Implement infection control measures and proper use of personal protective equipment.
Scholarship for the Nursing Discipline
- 4.1a Demonstrate an understanding of different approaches to scholarly practice.
- 4.1b Demonstrate application of different levels of evidence.
- 4.1c Apply theoretical framework(s)/models in practice.
- 4.1d Demonstrate an understanding of basic elements of the research process.
- 4.1e Participate in scholarly inquiry as a team member.
- 4.1f Evaluate research.
- 4.1g Communicate scholarly findings.
- 4.2a Evaluate clinical practice to generate questions to improve nursing care.
- 4.2b Evaluate appropriateness and strength of the evidence.
- 4.2c Use best evidence in practice.
- 4.2d Participate in the implementation of a practice change to improve nursing care.
- 4.2e Participate in the evaluation of outcomes and their implications for practice.
- 4.3a Explain the rationale for ethical research guidelines, including Institutional Review Board (IRB) guidelines.
- 4.3b Demonstrate ethical behaviors in scholarly projects including quality improvement and EBP initiatives.
- 4.3c Advocate for the protection of participants in the conduct of scholarly initiatives.
- 4.3d Recognize the impact of equity issues in research.
Quality and Safety
- 5.1a Recognize nursing’s essential role in improving healthcare quality and safety.
- 5.1b Identify sources and applications of national safety and quality standards to guide nursing practice.
- 5.1c Implement standardized, evidence-based processes for care delivery.
- 5.1d Interpret benchmark and unit outcome data to inform individual and microsystem practice.
- 5.1e Compare quality improvement methods in the delivery of patient care.
- 5.1f Identify strategies to improve outcomes of patient care in practice.
- 5.1g Participate in the implementation of a practice change.
- 5.1h Develop a plan for monitoring quality improvement change.
- 5.2a Describe the factors that create a culture of safety.
- 5.2b Articulate the nurse’s role within an interprofessional team in promoting safety and preventing errors and near misses.
- 5.2c Examine basic safety design principles to reduce risk of harm.
- 5.2d Assume accountability for reporting unsafe conditions, near misses, and errors to reduce harm.
- 5.2e Describe processes used in understanding causes of error.
- 5.2f Use national patient safety resources, initiatives, and regulations at the point of care.
- 5.3a Identify actual and potential level of risks to providers within the workplace.
- 5.3b Recognize how to prevent workplace violence and injury.
- 5.3c Promote policies for prevention of violence and risk mitigation.
- 5.3d Recognize one’s role in sustaining a just culture reflecting civility and respect.
Interprofessional Partnerships
- 6.1a Communicate the nurse’s roles and responsibilities clearly.
- 6.1b Use various communication tools and techniques effectively.
- 6.1c Elicit the perspectives of team members to inform person-centered care decision making.
- 6.1d Articulate impact of diversity, equity, and inclusion on team-based communications.
- 6.1e Communicate individual information in a professional, accurate, and timely manner.
- 6.1f Communicate as informed by legal, regulatory, and policy guidelines.
- 6.2a Apply principles of team dynamics, including team roles, to facilitate effective team functioning.
- 6.2b Delegate work to team members based on their roles and competency.
- 6.2c Engage in the work of the team as appropriate to one’s scope of practice and competency.
- 6.2d Recognize how one’s uniqueness (as a person and a nurse) contributes to effective interprofessional working relationships.
- 6.2e Apply principles of team leadership and management. performance to improve quality and assure safety.
- 6.2f Evaluate performance of individual and team to improve quality and promote safety.
- 6.3a Integrate the roles and responsibilities of healthcare professionals through interprofessional collaborative practice.
- 6.3b Leverage roles and abilities of team members to optimize care.
- 6.3c Communicate with team members to clarify responsibilities in executing plan of care.
- 6.4a Demonstrate an awareness of one’s biases and how they may affect mutual respect and communication with team members.
- 6.4b Demonstrate respect for the perspectives and experiences of other professions.
- 6.4c Engage in constructive communication to facilitate conflict management.
- 6.4d Collaborate with interprofessional team members to establish mutual healthcare goals for individuals, communities, or populations.
Systems-Based Practice
- 7.1a Describe organizational structure, mission, vision, philosophy, and values.
- 7.1b Explain the relationships of macrosystems, mesosystems, and microsystems.
- 7.1c Differentiate between various healthcare delivery environments across the continuum of care.
- 7.1d Recognize internal and external system processes that impact care coordination and transition of care.
- 7.2a Describe the financial and payment models of health care.
- 7.2b Recognize the impact of health disparities and social determinants of health on care outcomes.
- 7.2c Describe the impact of healthcare cost and payment models on the delivery, access, and quality of care.
- 7.2d Explain the relationship of policy, regulatory requirements, and economics on care outcomes.
- 7.2e Incorporate considerations of efficiency, value, and cost in providing care.
- 7.2f Identify the impact of differing system structures, leadership, and workforce needs on care outcomes.
- 7.3a Demonstrate a systematic approach for decision-making.
- 7.3b Use reported performance metrics to compare/monitor outcomes.
- 7.3c Participate in evaluating system effectiveness.
- 7.3d Recognize internal and external system processes and structures that perpetuate racism and other forms of discrimination within health care.
- 8.1a Identify the variety of information and communication technologies used in care settings.
- 8.1b Identify the basic concepts of electronic health, mobile health, and telehealth systems for enabling patient care.
- 8.1c Effectively use electronic communication tools.
- 8.1d Describe the appropriate use of multimedia applications in health care.
- 8.1e Demonstrate best practice use of social networking applications.
- 8.1f Explain the importance of nursing engagement in the planning and selection of healthcare technologies.
- 8.2a Enter accurate data when chronicling care.
- 8.2b Explain how data entered on one patient impacts public and population health data.
- 8.2c Use appropriate data when planning care.
- 8.2d Demonstrate the appropriate use of health information literacy assessments and improvement strategies.
- 8.2e Describe the importance of standardized nursing data to reflect the unique contribution of nursing practice.
- 8.3a Demonstrate appropriate use of information and communication technologies.
- 8.3b Evaluate how decision support tools impact clinical judgment and safe patient care.
- 8.3c Use information and communication technology in a manner that supports the nurse- patient relationship.
- 8.3d Examine how emerging technologies influence healthcare delivery and clinical decision making.
- 8.3e Identify impact of information and communication technology on quality and safety of care.
- 8.3f Identify the importance of reporting system processes and functional issues (error messages, mis-directions, device malfunctions, etc.) according to organizational policies and procedures.
- 8.4a Explain the role of communication technology in enhancing clinical information flows.
- 8.4b Describe how information and communication technology tools support patient and team communications.
- 8.4c Identify the basic concepts of electronic health, mobile health, and telehealth systems in enabling patient care.
- 8.4d Explain the impact of health information exchange, interoperability, and integration on health care.
- 8.5a Identify common risks associated with using information and communication technology.
- 8.5b Demonstrate ethical use of social networking applications.
- 8.5c Comply with legal and regulatory requirements while using communication and information technologies.
- 8.5d Educate patients on their rights to access, review, and correct personal data and medical records.
- 8.5e Discuss how clinical judgment and critical thinking must prevail in the presence of information and communication technologies.
- 8.5f Deliver care using remote technology.
Professionalism
- 9.1a Apply principles of professional nursing ethics and human rights in patient care and professional situations.
- 9.1b Reflect on one’s actions and their consequences.
- 9.1c Demonstrate ethical behaviors in practice.
- 9.1d Change behavior based on self and situational awareness.
- 9.1e Report unethical behaviors when observed.
- 9.1f Safeguard privacy, confidentiality, and autonomy in all interactions.
- 9.1g Advocate for the individual’s right to self- determination.
- 9.2a Employ the use of intentional presence to facilitate shared meaning of the experience between nurse and recipient of care.
- 9.2b Facilitate health and healing through compassionate caring.
- 9.2c Demonstrate empathy to the individual’s life experience.
- 9.2d Advocate for practices that advance diversity, equity, and inclusion.
- 9.2e Demonstrate cultural sensitivity and humility in practice.
- 9.2f Apply principles of therapeutic relationships and professional boundaries.
- 9.2g Communicate in a professional manner.
- 9.3a Engage in advocacy that promotes the best interest of the individual, community, and profession.
- 9.3b Demonstrate the moral courage to report concerns related to actual or potential hazards and/ or errors.
- 9.3c Demonstrate professional and personal honesty and integrity.
- 9.3d Take responsibility for one’s roles, decisions, obligations, actions, and care outcomes.
- 9.3e Engage in professional activities and/or organizations.
- 9.3f Demonstrate adherence to a culture of civility.
- 9.3g Advocate for social justice and health equity, including addressing the health of vulnerable populations.
- 9.3h Engage in peer evaluation.
- 9.4a Advocate for policies that promote health and prevent harm.
- 9.4b Adhere to the registered nurse scope and standards of practice.
- 9.4c Adhere to regulatory requirements and workplace policies consistent with one’s educational preparation.
- 9.5a Describe nursing’s professional identity and contributions to the healthcare team.
- 9.5b Demonstrate the core values of professional nursing identity.
- 9.5c Demonstrate sensitivity to the values of others.
- 9.5d Demonstrate ethical comportment and moral courage in decision making and actions.
- 9.5e Demonstrate emotional intelligence.
- 9.6a Demonstrate respect for diverse individual differences and diverse communities and populations
- 9.6b Demonstrate awareness of personal and professional values and conscious and unconscious biases.
- 9.6c Integrate core principles of social justice and human rights into practice.
Personal, Professional, and Leadership Development
- 10.1a Demonstrate healthy, self-care behaviors that promote wellness and resiliency.
- 10.1b Manage conflict between personal and professional responsibilities.
- 10.2a Engage in guided and spontaneous reflection of one’s practice.
- 10.2b Integrate comprehensive feedback to improve performance.
- 10.2c Commit to personal and professional development.
- 10.2d Expand personal knowledge to inform clinical judgment.
- 10.2e Identify role models and mentors to support professional growth.
- 10.2f Participate in ongoing activities that embrace principles of diversity, equity, inclusion, and anti- discrimination.
- 10.3a Compare and contrast leadership principles and theories.
- 10.3b Formulate a personal leadership style.
- 10.3c Demonstrate leadership behaviors in professional situations.
- 10.3d Demonstrate self-efficacy consistent with one’s professional development.
- 10.3e Use appropriate resources when dealing with ambiguity.
- 10.3f Modify one’s own leadership behaviors based on guided self-reflection.
- 10.3g Demonstrate self-awareness of one’s own implicit biases and their relationship to one’s culture and environment.
- 10.3h Communicate a consistent image of the nurse as a leader.
- 10.3i Recognize the importance of nursing’s contributions as leaders in practice and policy issues.
Master of Science in Nursing
Knowledge for Nursing Practice
Integration, translation, and application of established and evolving disciplinary nursing knowledge and ways of knowing, as well as knowledge from other disciplines, including a foundation in liberal arts and natural and social sciences. This distinguishes the practice of professional nursing and forms the basis for clinical judgment and innovation in nursing practice.
- 1.1e Translate evidence from nursing science as well as other sciences into practice
- 1.1f Demonstrate the application of nursing science to practice.
- 1.1g Integrate an understanding of nursing history in advancing nursing’s influence in health care.
- 1.2f Synthesize knowledge from nursing and other disciplines to inform education, practice, and research.
- 1.2g Apply a systematic and defendable approach to nursing practice decisions.
- 1.2h Employ ethical decision making to assess, intervene, and evaluate nursing care.
- 1.2i Demonstrate socially responsible leadership.
- 1.2j Translate theories from nursing and other disciplines to practice
- 1.3d Integrate foundational and advanced specialty knowledge into clinical reasoning.
- 1.3e Synthesize current and emerging evidence to Influence practice.
- 1.3f Analyze decision models from nursing and other knowledge domains to improve clinical judgment.
Person-Centered Care
Person-centered care focuses on the individual within multiple complicated contexts, including family and/or important others. Person-centered care is holistic, individualized, just, respectful, compassionate, coordinated, evidence-based, and developmentally appropriate. Person-centered care builds on a scientific body of knowledge that guides nursing practice regardless of specialty or functional area.
- 2.1d Promote caring relationships to effect positive outcomes.
- 2.1e Foster caring relationships.
- 2.2g Demonstrate advanced communication skills and techniques using a variety of modalities with diverse audiences.
- 2.2h Design evidence-based, person-centered engagement materials.
- 2.2i Apply individualized information, such as genetic/genomic, pharmacogenetic, and environmental exposure information in the delivery of personalized health care.
- 2.2j Facilitate difficult conversations and disclosure of sensitive information.
- 2.3h Demonstrate that one’s practice is informed by a comprehensive assessment appropriate to the functional area of advanced nursing practice.
- 2.4f Employ context driven, advanced reasoning to the diagnostic and decision-making process.
- 2.4g Integrate advanced scientific knowledge to guide decision making
- 2.5h Lead and collaborate with an interprofessional team to develop a comprehensive plan of care.
- 2.5i Prioritize risk mitigation strategies to prevent or reduce adverse outcomes.
- 2.5j Develop evidence-based interventions to improve outcomes and safety.
- 2.5k Incorporate innovations into practice when evidence is not available
- 2.6e Model best care practices to the team.
- 2.6f Monitor aggregate metrics to assure accountability for care outcomes.
- 2.6g Promote delivery of care that supports practice at the full scope of education.
- 2.6h Contribute to the development of policies and processes that promote transparency and accountability
- 2.6i Apply current and emerging evidence to the development of care guidelines/tools.
- 2.6j Ensure accountability throughout transitions of care across the health continuum.
- 2.7d Analyze data to identify gaps and inequities in care and monitor trends in outcomes.
- 2.7e Monitor epidemiological and system-level aggregate data to determine healthcare outcomes and trends.
- 2.7f Synthesize outcome data to inform evidencebased practice, guidelines, and policies.
- 2.8f Develop strategies that promote self-care management
- 2.8g Incorporate the use of current and emerging technologies to support self-care management.
- 2.8h Employ counseling techniques, including motivational interviewing, to advance wellness and self-care management
- 2.8i Evaluate adequacy of resources available to support self-care management.
- 2.8j Foster partnerships with community organizations to support self-care management.
- 2.9f Evaluate communication pathways among providers and others across settings, systems, and communities.
- 2.9g Develop strategies to optimize care coordination and transitions of care.
- 2.9h Guide the coordination of care across health systems.
- 2.9i Analyze system-level and public policy influence on care coordination.
- 2.9j Participate in system-level change to improve care coordination across settings
Population Health
Population health spans the healthcare delivery continuum from public health prevention to disease management of populations and describes collaborative activities with both traditional and non-traditional partnerships from affected communities, public health, industry, academia, health care, local government entities, and others for the improvement of equitable population health outcomes.
- 3.1j Assess the efficacy of a system’s capability to serve a target sub-population’s healthcare needs.
- 3.1k Analyze primary and secondary population health data for multiple populations against relevant benchmarks.
- 3.1l Use established or evolving methods to determine population-focused priorities for care.
- 3.1m Develop a collaborative approach with relevant stakeholders to address population healthcare needs, including evaluation methods.
- 3.1n Collaborate with appropriate stakeholders to implement a sociocultural and linguistically responsive intervention plan.
- 3.2d Ascertain collaborative opportunities for individuals and organizations to improve population health
- 3.2e Challenge biases and barriers that impact population health outcomes.
- 3.2f Evaluate the effectiveness of partnerships for achieving health equity.
- 3.2g Lead partnerships to improve population health outcomes.
- 3.2h Assess preparation and readiness of partners to organize during natural and manmade disasters.
- 3.3c Analyze cost-benefits of selected populationbased interventions.
- 3.3e Advocate for interventions that maximize costeffective, accessible, and equitable resources for populations.
- 3.3f Incorporate ethical principles in resource allocation in achieving equitable health.
- 3.4f Identify opportunities to influence the policy process.
- 3.4g Design comprehensive advocacy strategies to support the policy process.
- 3.4h Engage in strategies to influence policy change.
- 3.4i Contribute to policy development at the system, local, regional, or national levels.
- 3.4j Assess the impact of policy changes.
- 3.4k Evaluate the ability of policy to address disparities and inequities within segments of the population.
- 3.4l Evaluate the risks to population health associated with globalization.
- 3.5f Appraise advocacy priorities for a population.
- 3.5g Strategize with an interdisciplinary group and others to develop effective advocacy approaches.
- 3.5h Engage in relationship-building activities with stakeholders at any level of influence, including system, local, state, national, and/or global.
- 3.5i Demonstrate leadership skills to promote advocacy efforts that include principles of social justice, diversity, equity, and inclusion.
- 3.6f Collaboratively initiate rapid response activities to protect population health.
- 3.6g Participate in ethical decision making that includes diversity, equity, and inclusion in advanced preparedness to protect populations.
- 3.6h Collaborate with interdisciplinary teams to lead preparedness and mitigation efforts to protect population health with attention to the most vulnerable populations.
- 3.6i Coordinate the implementation of evidence-based infection control measures and proper use of personal protective equipment.
- 3.6j Contribute to system-level planning, decision making, and evaluation for disasters and public health emergencies.
Scholarship for the Nursing Discipline
The generation, synthesis, translation, application, and dissemination of nursing knowledge to improve health and transform health care.
- 4.1h Apply and critically evaluate advanced knowledge in a defined area of nursing practice.
- 4.1i Engage in scholarship to advance health.
- 4.1j Discern appropriate applications of quality improvement, research, and evaluation methodologies
- 4.1k Collaborate to advance one’s scholarship.
- 4.1l Disseminate one’s scholarship to diverse audiences using a variety of approaches or modalities.
- 4.1m Advocate within the interprofessional team and with other stakeholders for the contributions of nursing scholarship.
- 4.2f Use diverse sources of evidence to inform practice.
- 4.2g Lead the translation of evidence into practice.
- 4.2h Address opportunities for innovation and changes in practice.
- 4.2i Collaborate in the development of new/revised policy or regulation in the light of new evidence.
- 4.2j Articulate inconsistencies between practice policies and best evidence.
- 4.2k Evaluate outcomes and impact of new practices based on the evidence.
- 4.3e Identify and mitigate potential risks and areas of ethical concern in the conduct of scholarly activities.
- 4.3f Apply IRB guidelines throughout the scholarship process.
- 4.3g Ensure the protection of participants in the conduct of scholarship.
- 4.3h Implement processes that support ethical conduct in practice and scholarship.
- 4.3i Apply ethical principles to the dissemination of nursing scholarship.
Quality and Safety
Employment of established and emerging principles of safety and improvement science. Quality and safety, as core values of nursing practice, enhance quality and minimize risk of harm to patients and providers through both system effectiveness and individual performance.
- 5.1i Establish and incorporate data driven benchmarks to monitor system performance.
- 5.1j Use national safety resources to lead team-based change initiatives.
- 5.1k Integrate outcome metrics to inform change and policy recommendations.
- 5.1l Collaborate in analyzing organizational process improvement initiatives.
- 5.1m Lead the development of a business plan for quality improvement initiatives.
- 5.1o Advance quality improvement practices through dissemination of outcomes.
- 5.2g Evaluate the alignment of system data and comparative patient safety benchmarks.
- 5.2h Lead analysis of actual errors, near misses, and potential situations that would impact safety.
- 5.2i Design evidence-based interventions to mitigate risk.
- 5.2j Evaluate emergency preparedness system-level plans to protect safety.
- 5.3e Advocate for structures, policies, and processes that promote a culture of safety and prevent workplace risks and injury.
- 5.3f Foster a just culture reflecting civility and respect.
- 5.3g Create a safe and transparent culture for reporting incidents.
- 5.3h Role model and lead well-being and resiliency for self and team.
Interprofessional Partnerships
Intentional collaboration across professions and with care team members, patients, families, communities, and other stakeholders to optimize care, enhance the healthcare experience, and strengthen outcomes.
- 6.1g Evaluate effectiveness of interprofessional communication tools and techniques to support and improve the efficacy of team-based interactions.
- 6.1h Facilitate improvements in interprofessional communications of individual information (e.g. EHR).
- 6.1i Role model respect for diversity, equity, and inclusion in team-based communications.
- 6.1j Communicate nursing’s unique disciplinary knowledge to strengthen interprofessional partnerships.
- 6.1k Provide expert consultation for other members of the healthcare team in one’s area of practice.
- 6.1l Demonstrate capacity to resolve interprofessional conflict.
- 6.2g Integrate evidence-based strategies and processes to improve team effectiveness and outcomes.
- 6.2h Evaluate the impact of team dynamics and performance on desired outcomes.
- 6.2i Reflect on how one’s role and expertise influences team performance.
- 6.2j Foster positive team dynamics to strengthen desired outcomes.
- 6.3d Direct interprofessional activities and initiatives.
- 6.4e Practice self-assessment to mitigate conscious and implicit biases toward other team members.
- 6.4f Foster an environment that supports the constructive sharing of multiple perspectives and enhances interprofessional learning.
- 6.4g Integrate diversity, equity, and inclusion into team practices.
- 6.4h Manage disagreements, conflicts, and challenging conversations among team members.
- 6.4i Promote an environment that advances interprofessional learning.
Systems-Based Practice
Responding to and leading within complex systems of health care. Nurses effectively and proactively coordinate resources to provide safe, quality, and equitable care to diverse populations.
- 7.1e Participate in organizational strategic planning.
- 7.1f Participate in system-wide initiatives that improve care delivery and/or outcomes.
- 7.1g Analyze system-wide processes to optimize outcomes.
- 7.1h Design policies to impact health equity and structural racism within systems, communities, and populations.
- 7.2g Analyze relevant internal and external factors that drive healthcare costs and reimbursement.
- 7.2h Design practices that enhance value, access, quality, and cost-effectiveness.
- 7.2i Advocate for healthcare economic policies and regulations to enhance value, quality, and cost- effectiveness.
- 7.2j Formulate, document, and disseminate the return on investment for improvement initiatives collaboratively with an interdisciplinary team.
- 7.2k Recommend system-wide strategies that improve cost- effectiveness considering structure, leadership, and workforce needs.
- 7.2l Evaluate health policies based on an ethical framework considering cost-effectiveness, health equity, and care outcomes.
- 7.3e Apply innovative and evidence-based strategies focusing on system preparedness and capabilities.
- 7.3f Design system improvement strategies based on performance data and metrics.
- 7.3g Manage change to sustain system effectiveness.
- 7.3h Design system improvement strategies that address internal and external system processes and structures that perpetuate structural racism and other forms of discrimination in healthcare systems.
Information and communication technologies and informatics processes are used to provide care, gather data, form information to drive decision making, and support professionals as they expand knowledge and wisdom for practice. Informatics processes and technologies are used to manage and improve the delivery of safe, high-quality, and efficient healthcare services in accordance with best practice and professional and regulatory standards.
- 8.1g Identify best evidence and practices for the application of information and communication technologies to support care.
- 8.1h Evaluate the unintended consequences of information and communication technologies on care processes, communications, and information flow across care settings.
- 8.1i Propose a plan to influence the selection and implementation of new information and communication technologies.
- 8.1j Explore the fiscal impact of information and communication technologies on health care.
- 8.1k Identify the impact of information and communication technologies on workflow processes and healthcare outcomes.
- 8.2f Generate information and knowledge from health information technology databases.
- 8.2g Evaluate the use of communication technology to improve consumer health information literacy.
- 8.2h Use standardized data to evaluate decision- making and outcomes across all systems levels.
- 8.2i Clarify how the collection of standardized data advances the practice, undestanding, and value of nursing and support care.
- 8.2j Interpret primary and secondary data and other information to support care.
- 8.3g Evaluate the use of information and communication technology to address needs, gaps, and inefficiencies in care.
- 8.3h Formulate a plan to influence decision-making processes for selection, implementing, and evaluating support tools.
- 8.3i Appraise the role of information and communication technologies in engaging the patient and supporting the nurse-patient relationship.
- 8.3j Evaluate the potential uses and impact of emerging technologies in health care.
- 8.3k Pose strategies to reduce inequities in digital access to data and information.
- 8.4e Assess best practices for the use of advanced information and communication technologies to support patient and team communications.
- 8.4f Employ electronic health, mobile health, and telehealth systems to enable quality, ethical, and efficient patient care.
- 8.4g Evaluate the impact of health information exchange, interoperability, and integration to support patient-centered care.
- 8.5g Apply risk mitigation and security strategies to reduce misuse of information and communication technology.
- 8.5h Assess potential ethical and legal issues associated with the use of information and communication technology.
- 8.5i Recommend strategies to protect health information when using communication and information technology.
- 8.5j Promote patient engagement with their personal health data.
- 8.5k Advocate for policies and regulations that support the appropriate use of technologies impacting health care.
- 8.5l Analyze the impact of federal and state policies and regulation on health data and technology in care settings.
Professionalism
Formation and cultivation of a sustainable professional identity, including accountability, perspective, collaborative disposition, and comportment, that reflects nursing’s characteristics and values.
- 9.1h Analyze current policies and practices in the context of an ethical framework.
- 9.1i Model ethical behaviors in practice and leadership roles.
- 9.1j Suggest solutions when unethical behaviors are observed.
- 9.1k Assume accountability for working to resolve ethical dilemmas.
- 9.2h Foster opportunities for intentional presence in practice.
- 9.2i Identify innovative and evidence-based practices that promote person-centered care.
- 9.2j Advocate for practices that advance diversity, equity, and inclusion.
- 9.2k Model professional expectations for therapeutic relationships.
- 9.2l Facilitate communication that promotes a participatory approach.
- 9.3i Advocate for nursing’s professional responsibility for ensuring optimal care outcomes.
- 9.3j Demonstrate leadership skills when participating in professional activities and/or organizations.
- 9.3k Address actual or potential hazards and/or errors.
- 9.3l Foster a practice environment that promotes accountability for care outcomes.
- 9.3m Advocate for policies/practices that promote social justice and health equity.
- 9.3n Foster strategies that promote a culture of civility across a variety of settings.
- 9.3o Lead in the development of opportunities for professional and interprofessional activities.
- 9.4d Advocate for polices that enable nurses to practice to the full extent of their education.
- 9.4e Assess the interaction between regulatory agency requirements and quality, fiscal, and value-based indicators.
- 9.4f Evaluate the effect of legal and regulatory policies on nursing practice and healthcare outcomes.
- 9.4g Analyze efforts to change legal and regulatory policies that improve nursing practice and health outcomes.
- 9.4h Participate in the implementation of policies and regulations to improve the professional practice environment and healthcare outcomes.
- 9.5f Articulate nursing’s unique professional identity to other interprofessional team members and the public.
- 9.5g Evaluate practice environment to ensure that nursing core values are demonstrated.
- 9.5h Identify opportunities to lead with moral courage to influence team decision-making.
- 9.5i Engage in professional organizations that reflect nursing’s values and identity.
- 9.6d Model respect for diversity, equity, and inclusion for all team members.
- 9.6e Critique one’s personal and professional practices in the context of nursing’s core values.
- 9.6f Analyze the impact of structural and cultural influences on nursing’s professional identity.
- 9.6g Ensure that care provided by self and others is reflective of nursing’s core values.
- 9.6h Structure the practice environment to facilitate care that is culturally and linguistically appropriate.
- 9.6i Ensure self and others are accountable in upholding moral, legal, and humanistic principles related to health.
Personal, Professional, and Leadership Development
- 10.1c Contribute to an environment that promotes self-care, personal health, and well-being.
- 10.1d Evaluate the workplace environment to determine level of health and well-being.
- 10.2g Demonstrate cognitive flexibility in managing change within complex environments.
- 10.2h Mentor others in the development of their professional growth and accountability.
- 10.2i Foster activities that support a culture of lifelong learning.
- 10.2j Expand leadership skills through professional service.
- 10.3j Provide leadership to advance the nursing profession.
- 10.3k Influence intentional change guided by leadership principles and theories.
- 10.3l Evaluate the outcomes of intentional change.
- 10.3m Evaluate strategies/methods for peer review.
- 10.3n Participate in the evaluation of other members of the care team.
- 10.3o Demonstrate leadership skills in times of uncertainty and crisis.
- 10.3p Advocate for the promotion of social justice and eradication of structural racism and systematic inequity in nursing and society.
- 10.3q Advocate for the nursing profession in a manner that is consistent, positive, relevant, accurate, and distinctive.
Doctor of Nursing Practice
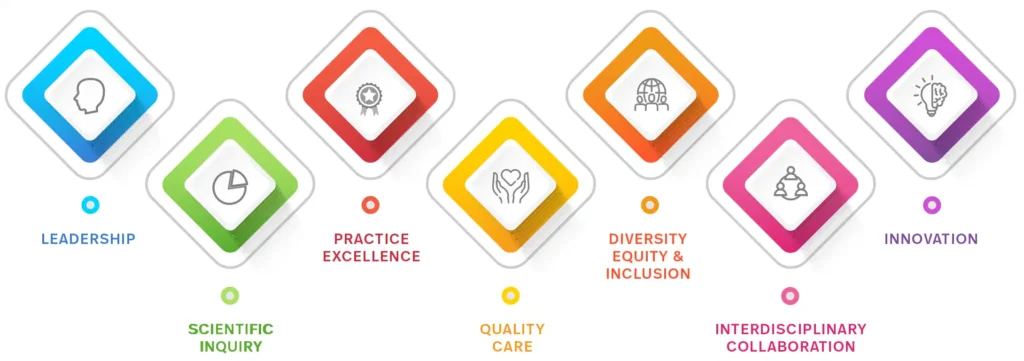
Leadership
Leads the design, implementation, evaluation, and dissemination of evidence-based practice improvement initiatives while promoting policies that advance health, social justice, and equity.
Scientific Enquiry
Critically analyzes complex clinical situations and practice environments to catalyze change in health care system.
Practice Excellence (Scholarship)
Translate evidence to develop new models for nursing practice that will transform healthcare and promote health and wellness.
Quality Care
Direct the development and implementation of social, economic, political and health policy to ensure quality and safety of health care delivery.
Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
Establish and evaluate cultural competency initiatives to promote equity and inclusion in healthcare and health outcomes.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Lead and diffuse interdisciplinary care coordination teams and collaborative efforts. (IOM, 2003)
Innovation
Evaluate and analyze the impact of health information technology implementation on organizations and nursing practice.
Practice Excellence (Systems)
Leads and coordinates resources within an institutional/community system to promote patient-centered, safe and effective, and equitable care to diverse populations.
Doctor of Nursing Practice in Nurse Anesthesia
Leadership
Leads the design, implementation, evaluation, and dissemination of evidence-based practice improvement initiatives while promoting policies that advance health, social justice, and equity.
Scientific Inquiry
Critically analyzes complex clinical situations and practice environments to catalyze change in health care system.
Practice Excellence
Translate evidence to develop new models for nursing practice that will transform health care.
Quality Care
Direct the development and implementation of social, economic, political and health policy to ensure quality of health care.
Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
Establish and evaluate cultural competency initiatives to promote equity and inclusion in healthcare and health outcomes.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Lead and diffuse interdisciplinary care coordination teams and collaborative efforts.(IOM, 2003)
Innovation
Evaluate and analyze the impact of health information technology implementation on organizations and nursing practice.
Doctor of Philosophy in Nursing
Students will be able to:
- Assume leadership in the promotion of health and well-being of urban populations nationally and internationally.
- Design a program of research that builds upon the historical and philosophical foundations of nursing science.
- Implement research studies that advance health science outcomes.
- Participate as a member of an interdisciplinary research team.
- Conduct research that demonstrates the theoretical, methodological, and analytical knowledge, skills, and strategies to address population health.
- Assume faculty, leader, and/or nurse scientist roles.
- Apply principles of professional research ethics and judgment in the conduct of research.